Sports injury
It refers to various types of injuries over various parts of the body incurred during any sporting activity. It can also be caused due to any strenuous activity. Certain parts of the body are more prone to damage from sports injuries.
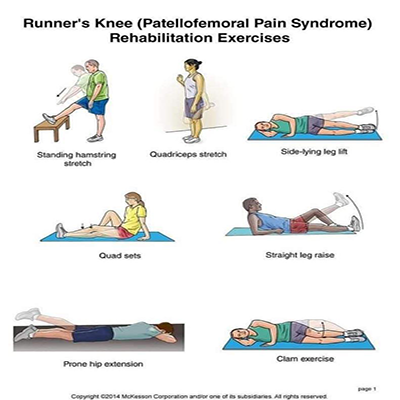
 Runner’s Knee
Runner’s Knee
Runner's knee means that one has dull pain around the front of the knee cap. This is where the knee connects with the lower end of the thighbone. Runner's knee may be caused by a structural defect, or a certain way of walking or running.
Other causes may include:
A kneecap that is too high in the knee joint, weak thigh muscles, Poor foot support, Excessive training or overuse and Injury. The Pain is usually in and around the kneecap that happens when you are active. Or pain occurs after sitting for a long time with the knees bent. It may cause weakness or feeling of instability in the legs. Rubbing, grinding, or clicking sound of the kneecap may be heard when one bends or straightens the knee. The Kneecap may be tender to the touch. A kneecap that is too high in the knee joint, weak thigh muscles, Poor foot support, Excessive training or overuse and Injury. The Pain is usually in and around the kneecap that happens when you are active. Or pain occurs after sitting for a long time with the knees bent. It may cause weakness or feeling of instability in the legs. Rubbing, grinding, or clicking sound of the kneecap may be heard when one bends or straightens the knee. The Kneecap may be tender to the touch.
Runner’s knee is the most common type of sports injury. The problem happens most commonly to runners, cyclists, swimmers, as well as people who practice aerobics, play football, basketball and volleyball. Overuse of the knee leads to irritation of the tendon below the knee-cap which results in this problem.
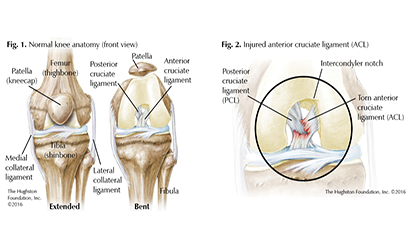 Knee Ligament Injuries
Knee Ligament Injuries
There are 4 major ligaments in the knee. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bones to each other and provide stability and strength to the joint. The four main ligaments in the knee connect the thighbone to the shin bone, and include,
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ligament, located in the center of the knee, that controls rotation and forward movement of the shin bone
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). The ligament, located in the back of the knee, that controls backward movement of the tibia shin bone.
Medial collateral ligament (MCL). The ligament that gives stability to the inner knee.
Lateral collateral ligament (LCL). The ligament that gives stability to the outer knee.
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most common ligaments to be injured. The ACL is often stretched and/or torn during a sudden twisting motion i.e, when the feet stay fixed one way, but the knees turn the other way. Basketball, and football are sports that have a higher risk of ACL injuries
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is also a common ligament to become injured in the knee. However, the PCL injury usually occurs with sudden, direct impact, such as in a car accident or during a football tackle.
Often, a cruciate ligament injury does not cause pain. Instead, the person may hear a popping sound as the injury occurs, followed by the leg buckling when trying to stand on it, and swelling. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently.
In addition to a complete medical history and physical examination, diagnostic procedures for a knee ligament injury may include the following:
• X-ray. A diagnostic test that uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film to rule out an injury to bone instead of, or in addition to, a ligament injury.
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body; can often determine damage or disease in bones and a surrounding ligament or muscle.
• Arthroscopy. A minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube (arthroscope) that is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen; used to evaluate any degenerative and/or arthritic changes in the joint; to detect bone diseases and tumors; to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation.
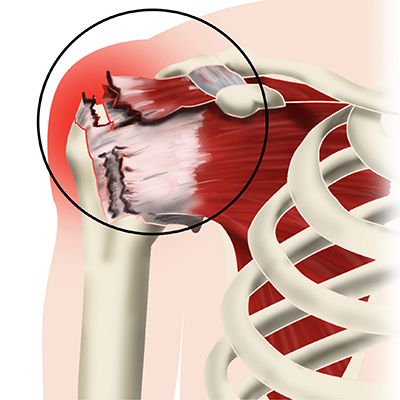 Shoulder Injury (Rotator Cuff Tear)
Shoulder Injury (Rotator Cuff Tear)
Such injury occur mostly during tennis, swimming, and volleyball. The main cause of these problems is the overuse of the shoulder, which loosens the rotator cuff (a group of tendons and muscles around the shoulder) .
Such injury occur mostly during tennis, swimming, and volleyball. The main cause of these problems is the overuse of the shoulder, which loosens the rotator cuff (a group of tendons and muscles around the shoulder) .
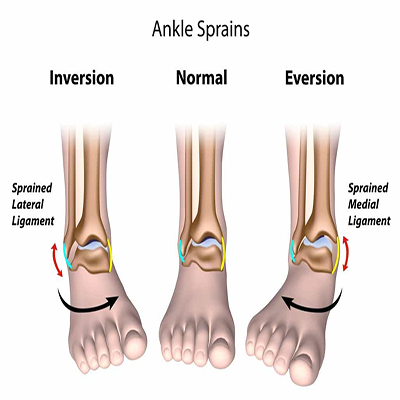 Ankle Sprain
Ankle Sprain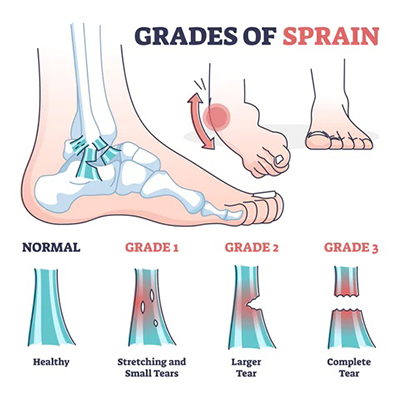
Ankle sprains are common to any activity that involves jumping, running or turning quickly (e.g., playing football, basketball etc). Such motion can lead to twisting of the ankle and possible tearing of a tendon/ligament
Tennis/Golfer’s Elbow: Tennis Elbow involves tendon degeneration in the elbow due to repeated backhand strokes common to tennis. This condition leads to pain on the outside of the elbow. Golfers Elbow impacts the inside of the elbow, due to the inflammation of the muscles responsible for forearm-flexing.
 Shin Splints
Shin Splints
Shin Splint is a pain on the inside of shinbone caused by inflammation of the surrounding muscles. These occur mostly in cases of inactive people who start working out and increase their intensity too fast.
 Groin injury
Groin injury
This refers to a strain the adductor muscles, situated in the upper thigh which help to pull the legs together and causes sharp pain and swelling on the inside of the thigh. This usually happens when one changes directions suddenly while running.
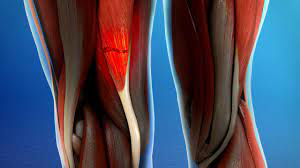 Hamstring Strain
Hamstring Strain
The hamstrings are the muscles behind your thighs. Hamstring strains most commonly occur due to inadequate warming up or excessive fatigue.
Prevention of Sports Injuries
One of the most important preventive step for sport injury is to choose the correct shoes and insoles, and keep replacing them regularly as they get worn out. Running on a softer surface like an indoor track rather than the road or pavement can also prevent a number of injuries. To prevent shoulder injuries, it is most important to strengthen your muscles through weight training before getting involved in active sports
Never resume your sports activities until your injury is fully healed. Restarting activity too soon can lead to further damage.
Treatment of Sports Injuries
 Medical therapy
Medical therapy
For pain control, using conservative care e.g., resting the impacted part, using hot/cold packs) along with medicines, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and adding a neuropathic agent in case of long standing of pain usually suffice.
Braces
Depending on the site of injury, different braces (e.g., thigh brace, elbow brace, arch brace, wrist brace, ankle brace, or knee brace) can be used to restrict the motion of the impacted part, control pain and speed up the recovery process.
Injections
Intra-lesional injections in the impacted part can provide significant pain relief in cases where medicines haven’t worked. Such interventional techniques should be followed by regular stretching and exercises for better results.
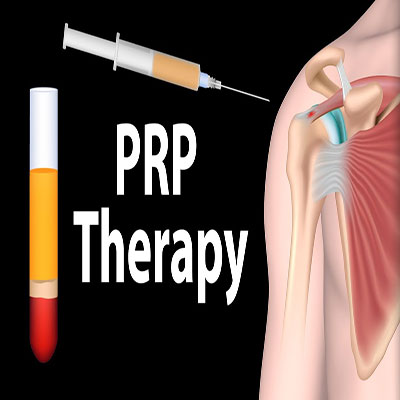 Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting platelets from the patient’s own blood to rebuild a damaged tendon or cartilage. It has been successful in not only relieving the pain, but also in starting the healing process quickly.The platelet-rich plasma is then injected into the damaged portion of the tendon or cartilage.