Headache
A headache is a pain in your head or face that’s often described as a pressure that’s throbbing, constant, sharp or dull. Headaches can differ greatly in regard to pain type, severity, location and frequency
There are several types of headaches, and tension headaches are the most common. While most headaches aren’t dangerous, certain types can be a sign of a serious underlying condition.
Types of headache
There are two main categories of headache, primary and secondary headaches.
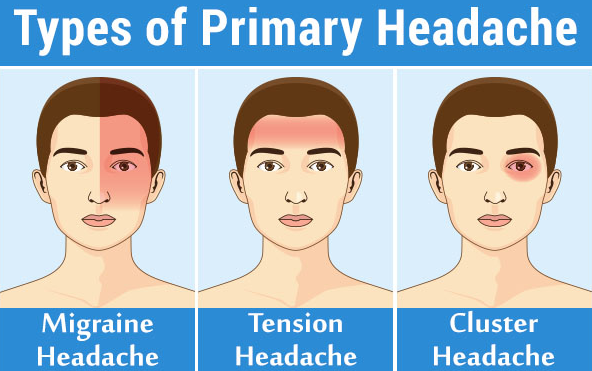 Primary headache
Primary headache
Over-activity of pain-sensitive areas in your head cause primary headaches. They’re not a symptom of or caused by an underlying medical condition. Some people may have genes that make them more likely to develop primary headaches.
It include Tension-type headaches (most common type of headache),Migraine headaches, Cluster headaches, New daily persistent headaches (NDPH).
Primary headaches can be triggered by lifestyle factors like:
• Alcohol, particularly red wine
• Certain foods, such as processed meats that contain nitrates (food-triggered headaches).
• Consuming nicotine (nicotine headache).
• Changes in sleep or lack of sleep.
• Poor posture.
• Physical activity, such as exercise (exertion headaches).
• Skipped meals (hunger headache).
• Coughing, sneezing, blowing your nose, straining (such as when having a bowel movement), or laughing or crying vigorously (primary cough headaches).
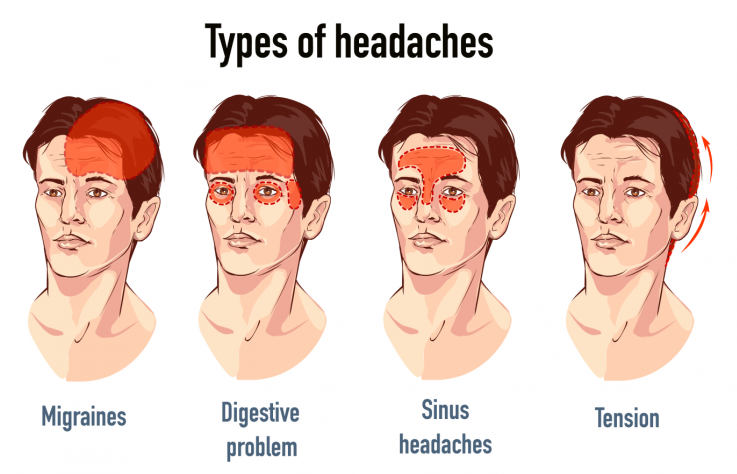 Secondary headache
Secondary headache
An underlying medical condition can cause secondary headaches. Types of secondary headaches that aren’t necessarily dangerous and resolve once the underlying condition is treated include:
• Dehydration headache.
• Sinus headaches.
• Drug overdose headaches
Some types of secondary headaches that can be a sign of a serious or potentially life -threatening condition include:
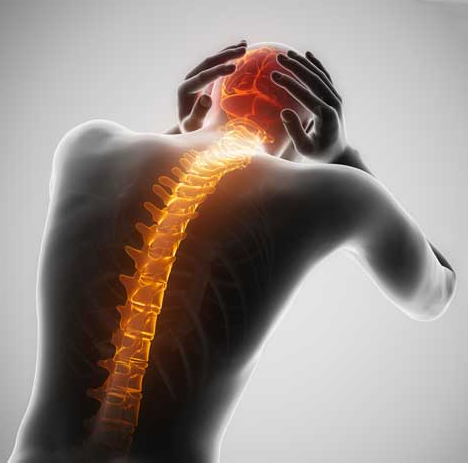 Spinal headaches:
Spinal headaches: Spinal headaches are intense headaches that occur when spinal fluid leaks out of the membrane covering your spinal cord, usually after a spinal tap. Most spinal headaches can be treated at home, but prolonged, untreated spinal headaches can cause life -threatening complications, including subdural hematoma and seizures.
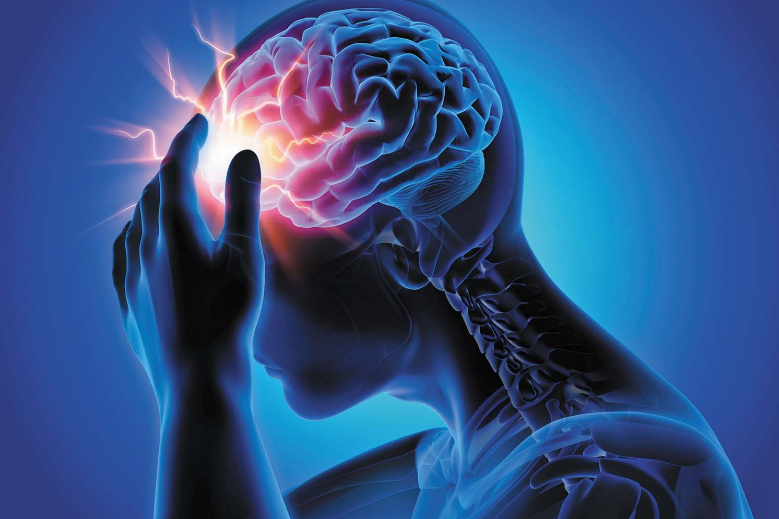 Thunderclap headaches:
Thunderclap headaches: A thunderclap headache is an extremely painful headache that comes on suddenly, like a clap of thunder. This type of headache reaches its most intense pain within one minute and lasts at least five minutes. While thunderclap headaches can sometimes be harmless, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention.
They can be a sign of:
• Head injury.
• Brain bleed.
• Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome.
• A sudden, severe rise in blood pressure.
Migraine
Migraine is a condition that causes episodes of headache attacks. Other symptoms such as feeling nausea or vomiting are common between attacks of migraine.
About 1 in 4 women and about 1 in 12 men develop migraine at some point in their lives. Some people have frequent attacks, sometimes several times a week. In some people, the migraine attacks stop in later adult life. However, in some cases the attacks continue throughout life.
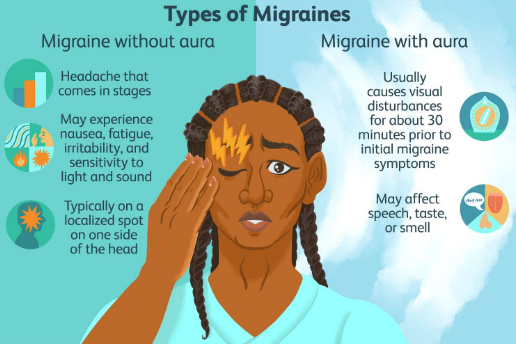 Types of migraine
Types of migraine
Migraine attack without aura
The headache is usually on one side of the head, typically at the front and some time on both sides.
Sometimes it starts on one side, and then spreads all over the head. The pain can be moderate or severe and is often described as throbbing or pulsating. Movements of the head may make it worse. It may begin at any time of the day or night. It gradually gets worse over 2-12 hours and then gradually eases off. It can last from 4 to 72 hours, Other complaints that are common include, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, Blurred vision, sweating, etc.
Migraine attack with aura
The complaints are the same as those in migraine without aura, but also include a warning sign or aura before the headache begins.
Visual aura is the most common type of aura. Eg. temporary loss of part of vision, flashes of light, Numbness, pins and needles are the second most common type of aura.
Facial aura: Numbness usually starts in one or both hands, travels up the arm and can involve the face, lips, and tongue.
Speech aura: Problems with speech are the third most common type of aura. Other types of aura include an odd smell, food cravings, a feeling of well-being, and other odd sensations.
Each aura usually lasts just a few minutes before going, but can last up to 60 minutes. The aura usually goes before the headache begins. The headache usually develops within 60 minutes of the end of the aura, but it may develop a lot sooner than that – often straight afterwards.
Diagnosis
Migraine is usually diagnosed by the typical complaints. There is no test to confirm migraine.
Cause
The cause of migraine headache is not clear. It is believed blood vessels in parts of the brain become narrower and lead to aura and open wide soon afterwards, which accounted for the headache. It is now thought that some chemical activity in the brain send out confusing signals which cause the headache.
Treatment
Medical therapy
Paracetamol or aspirin works well for many migraine attacks. Take a dose as early as possible after symptoms begin. If painkillers are taken early enough, they often reduce the severity of the headache, or stop it completely. Other painkillers probably work better than paracetamol. They include ibuprofen and Naproxen.
Injections
For treating chronic migraines and headaches, injections like the Occipital nerve block and Sphenopalatine ganglion block have proven to be effective. BOTOX® injections are the first and only FDA-approved preventive treatment proven to reduce migraine and headache days every month.