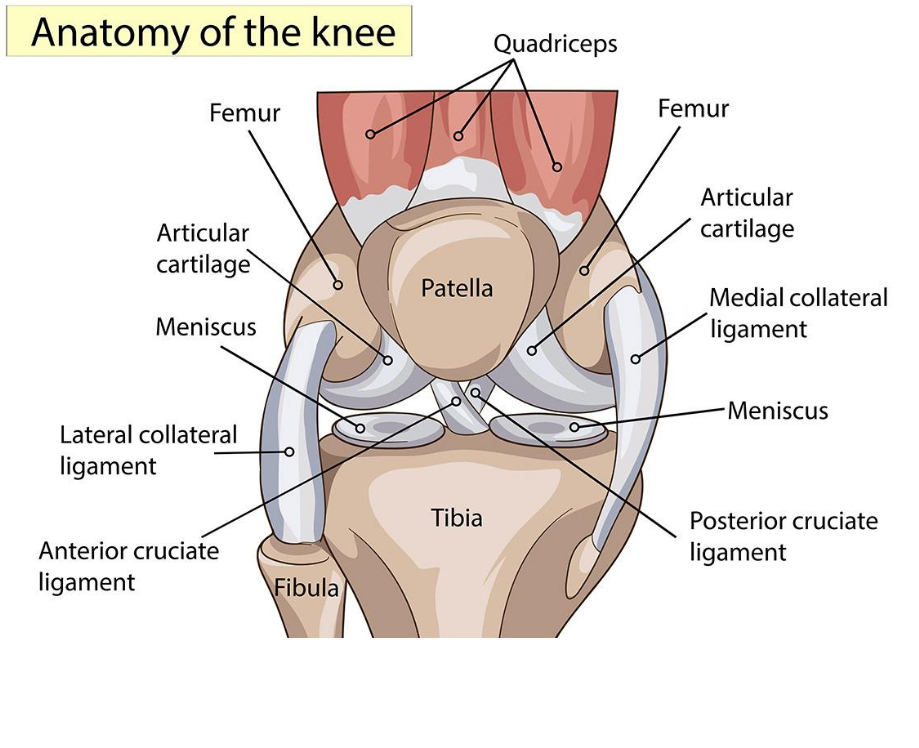
Knee joint osteoarthritis is a long standing condition that causes swelling and stiffness of the knee joint. Complaints include redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness and pain.
There is a gradual wearing down of the tough cartilage in the knee joint space. Knee joint osteoarthritis usually develops over years and often is found in a person who have had a knee infection or injury and those who are obese.
The bones around the cartilage grow thicker and develop bony spurs. This leads to increased friction between the bones and make the movement in your knee rough. This can also lead to problems with the synovium (a membrane within your knee that produces a viscous liquid to keep the joint movement smooth). This membrane can become inflamed and make too much fluid, leading to swelling of the joint. In the most severe cases, the knee can become deformed as the continued friction wears away the bone.
Rheumatoid arthritis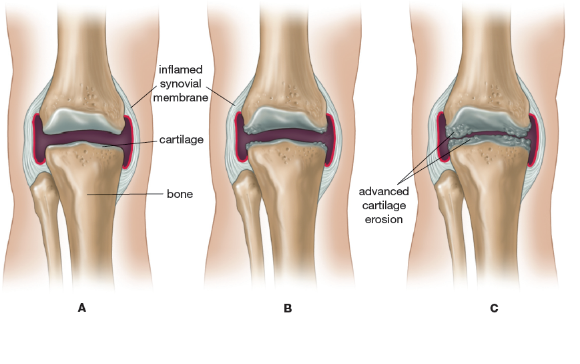
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect joints on both sides of the body (both knees, both hands and/or both wrists). In rheumatoid arthritis, your body’s cells attack your own tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis affects three to five times more women than men and often presents between the ages of 20 and 50. Over time, rheumatoid arthritis can cause cartilage to wear away, swelling in the synovium and excess fluid in the knee. In later stages, bones can rub against each other.
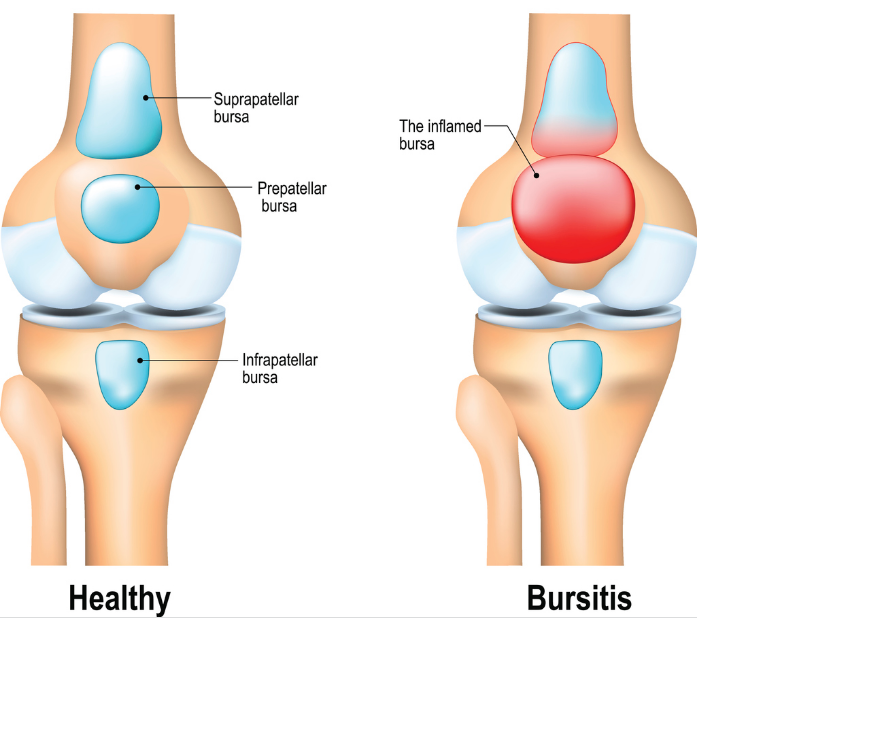 Bursitis
Bursitis
Bursitis is the swelling and redness of any of the fluid-filled sac or bursae over the body’s joints. This is usually caused by repetitive stress such as kneeling.
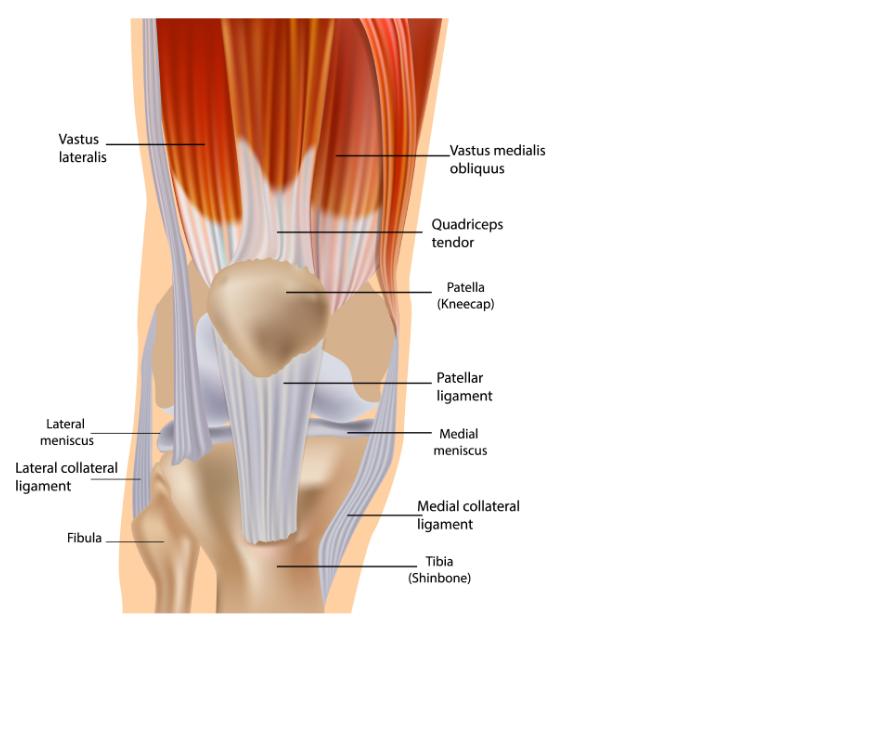 Tendonitis
Tendonitis
The tendons are the tissues connecting the muscles to a bone at the knee and other joints. It can swell up and become painful by repetitive, strenuous movement. Tendonitis is a common sports injury, caused by overuse of the same muscles around a joint. Patellar tendonitis is an inflammation or irritation of the tendon between the knee cap and the shin bone.
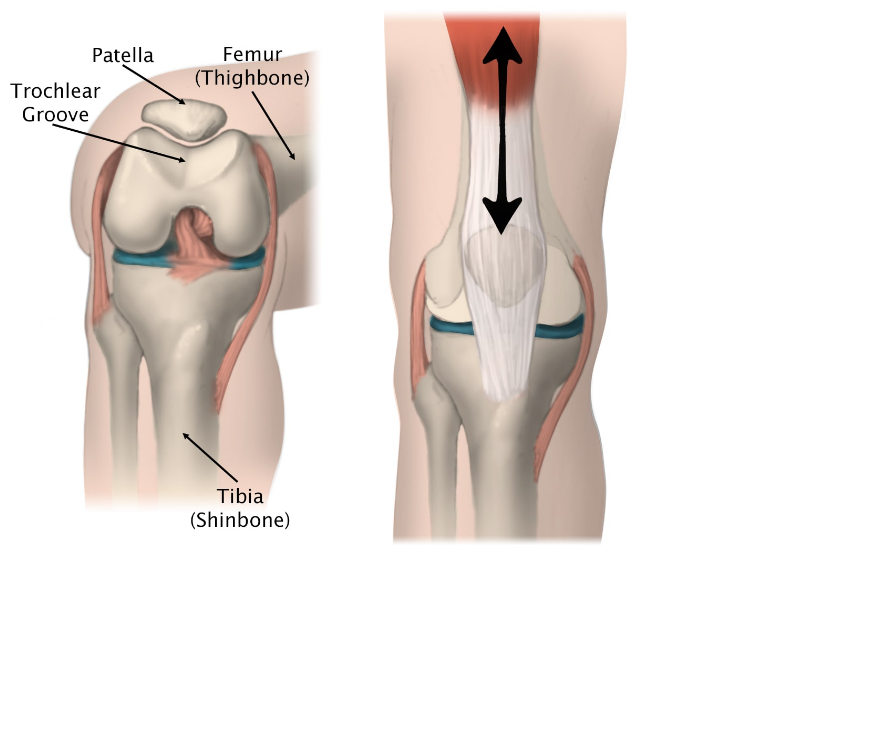 Patellofemoral pain syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
Pain & discomfort while moving up and down stairs, jumping or squatting may be because of patellofemoral pain syndrome. It is felt toward the front of the knee. It can cause a grinding sensation while bending or straightening the leg, and can cause the knee to occasionally buckle. Patellofemoral pain syndrome may be caused by overuse, injury, excess weight or when the cartilage in the knee cap is worn significantly.
 Injury to the knee
Injury to the knee
Knee injuries can be the result of sports related trauma. They typically involve the ligaments that hold two of the bones of the knee joint causing Ligament & Meniscal injuries.
 Knee Pain Treatment
Rest
Knee Pain Treatment
Rest
When the knee is injured or swelled up, as in bursitis, tendonitis or arthritis, it’s important to rest the joint and avoid overuse. This means keeping the knee joint straight or in positions that limit bending.
Ice/Heat fomentation
Applying ice or cold packs to the knee can reduce pain and swelling, especially after an injury. Once swelling reduces, heat may be used to help relax and loosen the tissues around the joint.
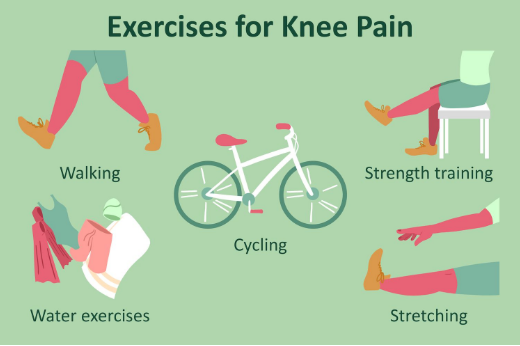
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can help you recover from the injury and decrease the pain. They include low-impact stretches and exercises that can strengthen muscles around your knee, improve stability and flexibility, and reduce pressure on the joint.
Pain killers
Over-the-counter pain killer medicines can help relieve knee pain, including ibuprofen and paracetamol.
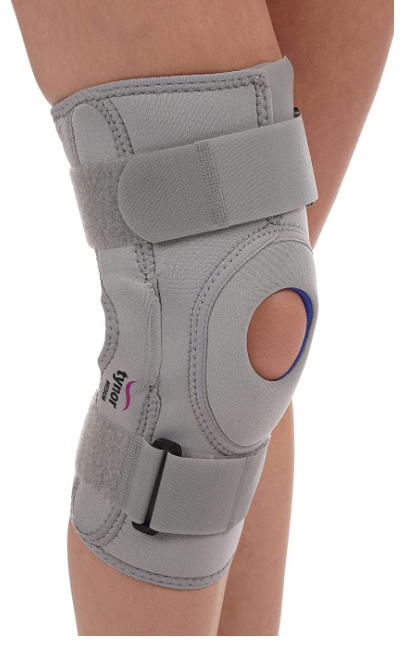 Knee supporting brace
Knee supporting brace
Appropriate Knee braces wrap around the knee and leg and help limit unwanted movement while supporting the knee. They are commonly used when knee ligaments are weak, and help to keep the knee stable.
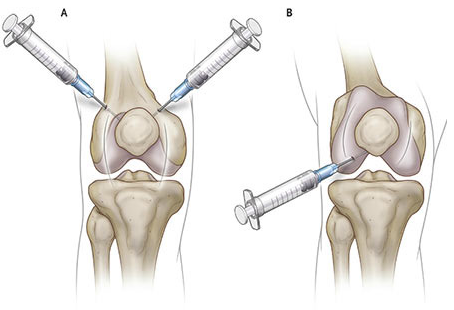 Injections in the Knee Joint
Injections in the Knee Joint
Potent drugs can be injected inside the knee to reduce pain and swelling.Ozone Gas can also be injected into the knee to reduce pain.
Another injection that can provide relief from knee pain is visco-supplementation. It involves injecting a lubricant into the knee joint. This lubricates and adds cushioning to the knee joint, allowing bones to move more easily and reducing friction. It is a very useful and effective solution for mild to moderate OA.
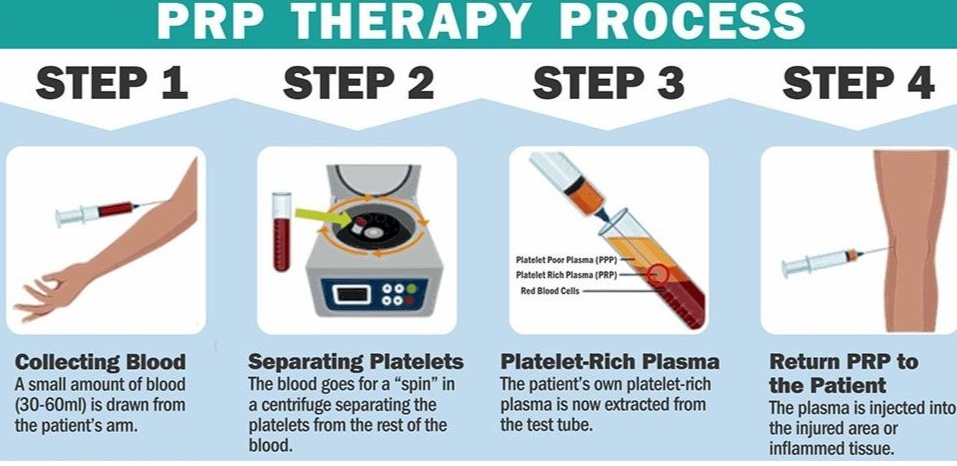 Stem Cell/Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy
Stem Cell/Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting platelets from the patient’s own blood to rebuild a damaged tendon or cartilage. It not only relieves the pain, but also starts the healing process quickly.
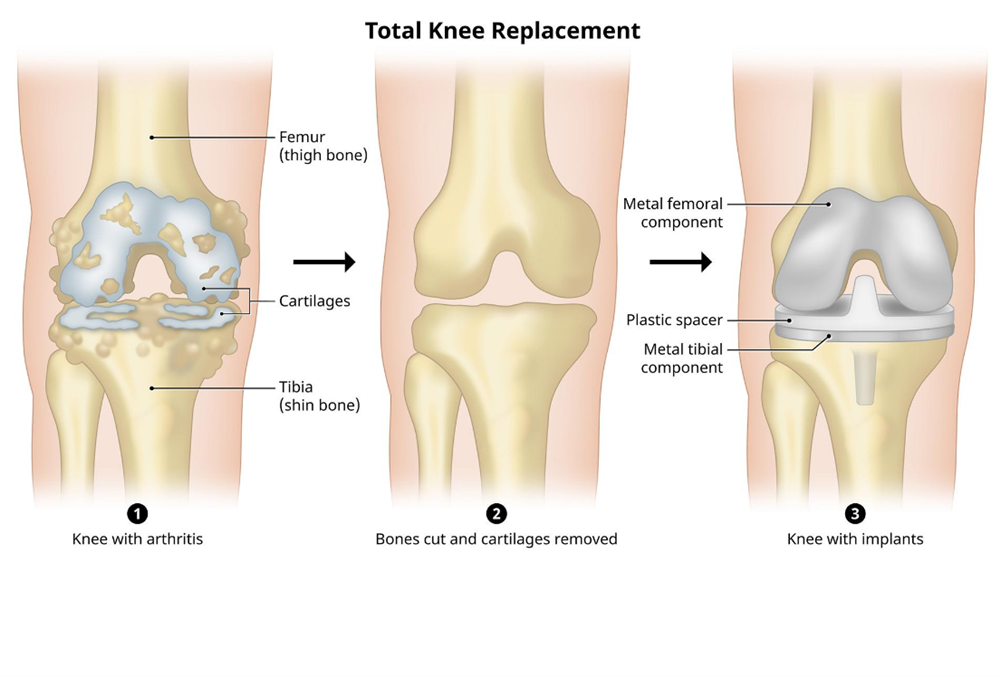 Surgery
Surgery
These include partial and total knee replacements in case of severe osteoarthritis of the knee joint or Rheumatoid arthritis of knee joint. In cases of ligament tear, one can opt for arthroscopic repair.